Both Modafinil and Adderall are central nervous system medications with similar mechanisms of actions and are used in treatment of narcolepsy. The difference lies in their specific pharmacodynamics and the intensity of their impact on the human mind.
Mode of action
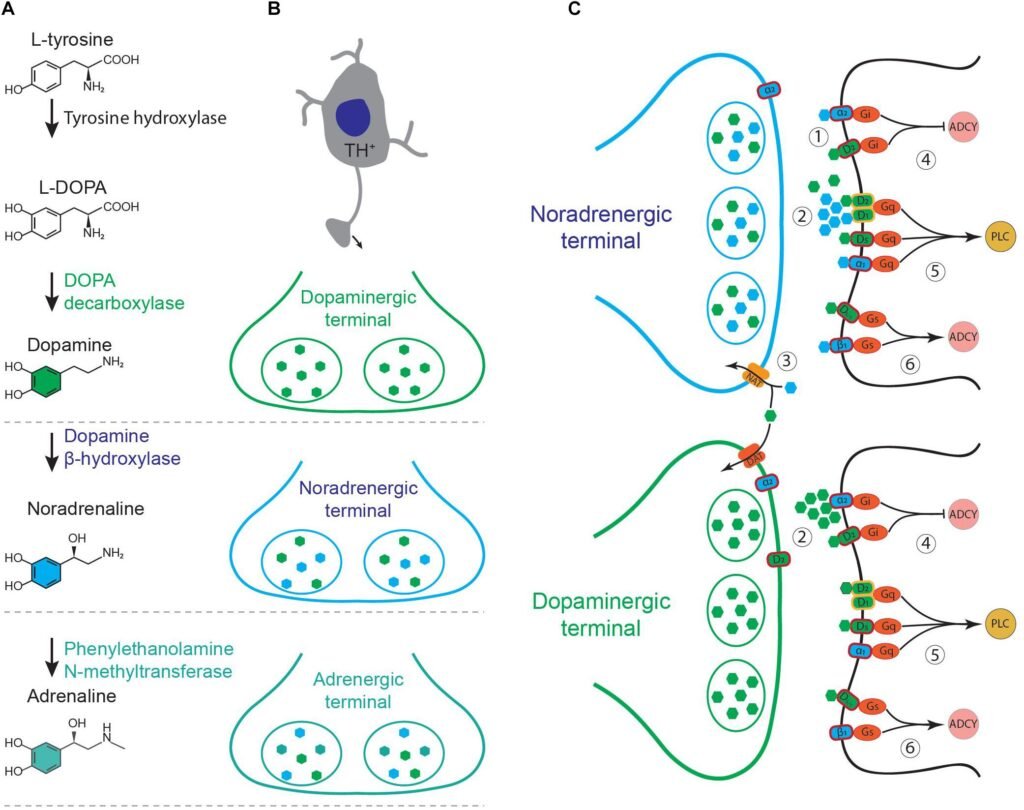
Modafinil or Provigil is a wakefulness stimulating medication that stimulates the dopamine and norepinephrine, and orexin receptors of the brain to exert its neuroprotective impact on the mind.
Adderall is an Amphetamine-Dextroamphetamine derivative that predominantly stimulates the release of norepinephrine in the adrenergic receptor sites. Norepinephrine is an important neurotransmitter in the CNS that helps in managing stress and dealing with cognitive functions.
Amphetamine, the chief constituent of Adderall, works on the alpha and beta-adrenergic receptor sites to regulate the blood pressure and impact mood, arousal, and memory.
Animal studies comparing the locomotor effects of Modafinil with Dexamphetamine ( Adderall Derivative in conjunction with D1 (modulating motor behavior, locomotion, and cognitive processes )and D2 antagonists ( modulating locomotion, sleep, memory, attention, and learning ) have found that the behavioral effects of Amphetamine can be suppressed by D1 and D2 antagonist but they could not impact the behavioral impacts of Modafinil.
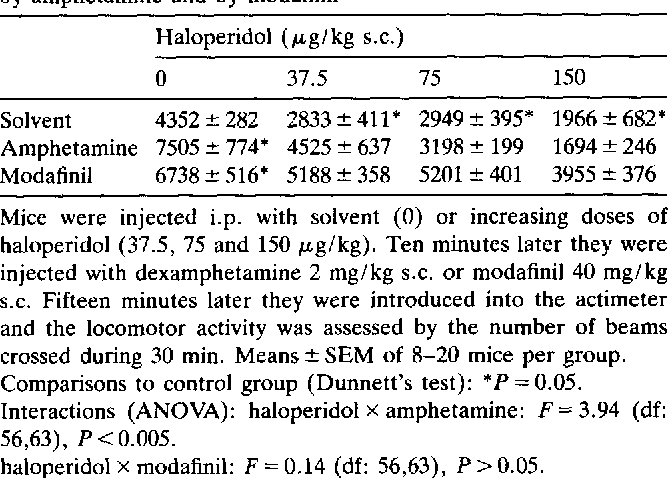

Only a very high dose of D2 antagonist – in this case SCH 23390 could moderately impact the locomotor impacts of Modafinil.
In the study, anti-monoaminergic reserpine ( a medication used to treat blood pressure ) was used that produced akinesia or immobility in certain parts of the body. Amphetamine was able to reverse the akinesia impact successfully, but Modafinil did not impact the locomotor effect.
Further, Amphetamine caused a spontaneous dopamine release, but Modafinil did not produce any such impact.
Based on the study, we can conclude that Modafinil is a milder stimulant than Adderall, and the two medications have different dopaminergic actions that impact their use in people with irregular CNS activity.
Adderall is stronger than Modafinil and thus effective in individuals with ADD, ADHD diagnosed individuals to control behavioural problems, increase ability to pay attention and stay focussed on an activity.
Modafinil is a wakefulness-promoting medication that helps you stay awake along with improving your decision making skills. Modafinil further selectively impacts working memory but does not increase the dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens , a behaviour observed in drugs of abuse as the nucleus accumbens plays an important role in learning, memory, reward, and motivation. Because of this, Modafinil is safer than Adderall and has a lower abuse potential.

Antioxidative and Neuroprotective Effects
The Neuroprotective and Antioxidative effects of Modafinil are more pronounced than those of Adderall, with a positive impact on reducing fatigue.
Parkinson’s impacts 500,000 Americans with significant impact on the treatment costs and indirect impacts like loss of productivity.
Medications help offer symptomatic relief but often fail in dealing with relieving fatigue. Additionally, Levodopa, the primary treatment option for Parkinson’s, can induce excessive daytime sleepiness with resulting impairment in cognitive abilities.
Researchers have observed through in-vitro trials that Modafinil use in Parkinson’s patients repairs the impaired striatum Dopamine, a characteristic feature in Parkinson’s patients associated with motor problems, while showing an ameliorating effect on the 5HT or Serotonin.
In comparison, Adderall use in Parkinson’s is limited because of the preexisting striatal Dopamine deficiency.
Based on their impact on the neurons and neurotransmitters, it can be safe to conclude that Modafinil and Amphetamine are two differently-acting stimulants with different impacts on learning and memory.
They further differ in their pharmacodynamics and potential for abuse and addiction. Further research needs to be conducted to evaluate their roles in different neuropsychiatric fields.





